hyperprogressionは存在しない説
論文 免疫チェックポイント阻害剤
免疫チェックポイント阻害剤を投与したことによって腫瘍が縮小するどころか、逆に急激に腫瘍の増大・増悪を認める事例が多数報告され、免疫チェックポイント阻害剤によるhyperprogressionあるいはhyperprogressive disease(HPD)と呼ばれたりします。
このHyperprogressionは、免疫という神の領域のブラックボックスに人が手を突っ込んだことに対する怒りや祟りのように喩えられることもある、未解明で不可解な現象ではありますが、果たしてこのhyperprogressionという現象は本当に免疫チェックポイント阻害剤の投与によって引き起こされているのかということに関する報告です。

Background Retrospective studies have suggested a potential risk of hyperprogressive disease (HPD) in patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). We compared the incidence of HPD during treatment with nivolumab±ipilimumab versus natural tumor progression with placebo in post hoc analyses of two randomized, double-blind clinical trials.
Methods ATTRACTION-2 randomized patients with advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer (GC/GEJC) and progression on ≥2 prior regimens to nivolumab 3 mg/kg Q2W or placebo. CheckMate 451 randomized patients with extensive-disease small cell lung cancer (ED SCLC) and ongoing complete/partial response or stable disease after first-line chemotherapy to nivolumab 240 mg Q2W, nivolumab 1 mg/kg+ipilimumab 3 mg/kg Q3W for four doses then nivolumab 240 mg Q2W, or placebo. Patients receiving ≥1 dose of study drug and with tumor scans at baseline and the first on-treatment evaluation were included in the HPD analyses. HPD definitions were ≥20%, ≥50%, and ≥100% increase in target lesion sum of the longest diameters (SLD) at the first on-treatment assessment.
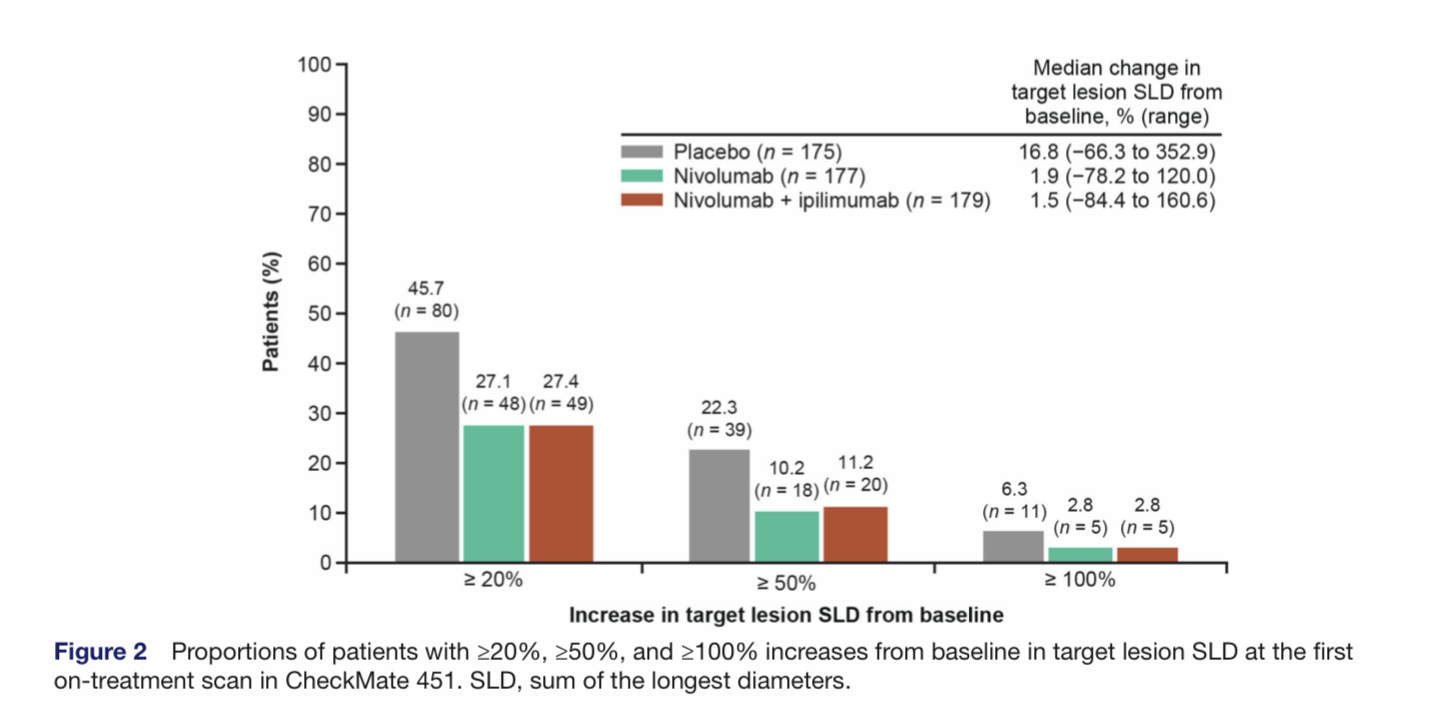
Results In the ATTRACTION-2 HPD-evaluable population, 243 patients received nivolumab and 115 placebo. Fewer patients receiving nivolumab versus placebo had increases in SLD ≥20% (33.7% vs 46.1%) and ≥50% (6.2% vs 11.3%); similar proportions had increases in SLD ≥100% (1.6% vs 1.7%). In the CheckMate 451 HPD-evaluable population, 177 patients received nivolumab, 179 nivolumab+ipilimumab, and 175 placebo. Fewer patients receiving nivolumab or nivolumab+ipilimumab versus placebo had increases in SLD ≥20% (27.1%, 27.4% vs 45.7%), ≥50% (10.2%, 11.2% vs 22.3%), and ≥100% (2.8%, 2.8% vs 6.3%).
Conclusions Nivolumab±ipilimumab was not associated with an increased rate of progression versus placebo in patients with GC, GEJC, or ED SCLC, suggesting that previous reports of HPD may reflect the natural disease course in some patients rather than ICI-mediated progression.
Trial registration number [NCT02538666][1]; [NCT02267343][2].
Bristol Myers Squibb’s policy on data sharing can be found at <https://www.bms.com/researchers-and-partners/independent-research/data-sharing-request-process.html>.
[1]: /lookup/external-ref?link_type=CLINTRIALGOV&access_num=NCT02538666&atom=%2Fjitc%2F10%2F4%2Fe004273.atom
[2]: /lookup/external-ref?link_type=CLINTRIALGOV&access_num=NCT02267343&atom=%2Fjitc%2F10%2F4%2Fe004273.atom
https://jitc.bmj.com/content/10/4/e004273
中国からの論文で、上部消化管癌を対象に実施されたATTRACTION-2試験とCheckMate-451試験を基にした解析です。ニボルマブやイピリムマブを投与された患者とプラセボ群での、初回効果判定までにそれぞれ20%、50%、100%以上の腫瘍径の増大を示した患者の割合を比較しています。カットオフ値を20%、50%、100%のいずれにしても、免疫チェックポイント阻害剤で腫瘍が急激に増大した群は確かに存在するのですがプラセボ群での同様の増大を示した患者の割合よりは低くなっています。
これらの結果から、hyperprogressionは免疫チェックポイント阻害剤の投与によって引き起こされたように考えられていたが、その実は免疫チェックポイント阻害剤の投与と関係ないプラセボ群でも見られる現象であり、単なる腫瘍としての自然経過でそのような急激な増悪が起こり得るのではないかと考察されています。
言われてみれば確かに従来の殺細胞性抗腫瘍剤でも投与後の急激な増悪は見られますし、治療を開始する前の精査中に激しく進行する症例も見られますので、免疫チェックポイント阻害剤の投与は関係がな意かもしれません。言葉だけが一人歩きしていた、ということでしょうか?
余談
そういえばもう一つ、腫瘍には免疫チェックポイント阻害剤が効いているのに画像的には腫瘍が増大しているように見えるpseudoprogressionという現象も、本当にどれだけ存在するのかは気になっているのですが…。いったんは増大したようには見えるものの、そのまま治療を継続してゆくといずれ腫瘍は縮小に転じるという現象は、確かに免疫チェックポイント阻害剤に限らず、これも殺細胞性抗腫瘍薬にも見られる現象ですので…。
この記事に対するコメント
このページには、まだコメントはありません。
更新日:2022-04-22 閲覧数:528 views.